Why feedback is important in die casting cycle: Zero Porosity Management by Rahat A Bhatia
When it comes to die casting, the pursuit of perfection is the ultimate goal. And in the realm of die casting, minimizing porosity is an essential step towards achieving excellence. Rahat A Bhatia’s groundbreaking book, “Zero Porosity Management,” offers a profound exploration of porosity control in die casting. In this SEO-optimized blog post, we’ll delve into the key insights from the book while ensuring that the book and author remain in the spotlight for search engine visibility.
The Complexity of Porosity Control
Controlling porosity in die casting is a complex process. Numerous variables come into play, and there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Standardizing parameters across every die-cast part is nearly impossible due to the multitude of variables involved. So, where can we begin to standardize and optimize the process? Rahat A Bhatia suggests focusing on the design aspect.
Bridging the Gap Between Design and Reality
In the real world of die casting, things don’t always go as planned. Even the most meticulously designed processes can encounter unexpected challenges on the shop floor. “Zero Porosity Management” explores the practical aspects of die casting and offers insights into dealing with real-life, unpredictable scenarios. The book raises the question: Can we create a framework to capture these situations and adjust parameters for optimization? Is it possible to make this framework work effectively under unpredictable conditions? Let’s find out.
The Vital Role of Feedback Mechanisms
 One of the critical challenges in die casting is that product, tool, gate, and process parameters are often designed based on ideal conditions that rarely exist on the shop floor. The book emphasizes that porosity often takes a back seat in product design discussions, even though it’s interconnected with factors like functionality, strength, durability, safety, and weight reduction.
One of the critical challenges in die casting is that product, tool, gate, and process parameters are often designed based on ideal conditions that rarely exist on the shop floor. The book emphasizes that porosity often takes a back seat in product design discussions, even though it’s interconnected with factors like functionality, strength, durability, safety, and weight reduction.
In response to these challenges, innovative die casting companies worldwide are investing in various technologies and innovations. They’re upgrading their design software, utilizing advanced simulations, and adopting state-of-the-art die-casting machines. They’re also implementing monitoring systems, data analysis, and AI-driven solutions to maintain control over the die-casting process.
Industry Insiders on Die Casting Industry 4.0 & AI
Industry experts recognize the potential of technologies like Industry 4.0 and AI in revolutionizing die casting. With advancements in monitoring temperature, thermal equilibrium, and visual inspection using cutting-edge tools, die casters can spot and analyze variations. By controlling these variations, they can significantly reduce porosity, leading to higher-quality castings.
To embark on this journey of improvement, here are some key questions to consider regarding feedback and monitoring in your die-casting unit:
- Is there a comprehensive monitoring mechanism in place for your die-casting ecosystem?
- Are you capturing and analyzing data effectively?
- Are actionable insights being derived from the gathered data?
- Do you have a mechanism for providing feedback to customers regarding part design?
- Is there a structured feedback and correction process for tool and gate design, process parameters, and die maintenance?
The Design and Optimization Cycles
The book introduces two essential cycles in the die casting process: the Design Cycle and the Optimization Cycle.
Design Cycle
The Design Cycle involves making decisions for new product development. It includes product design, tool and gate design, and process parameters based on calculations, experience, and simulations. This is typically a one-time exercise for a new product.
Optimization Cycle
The Optimization Cycle focuses on existing products and aims for improvements, corrections, or modifications. It involves revisiting parameters such as tool, gate, and process design based on real-time shop floor conditions, including melting, pouring, injection, die performance, and more. Two approaches can be followed within this cycle:
Corrective Approach
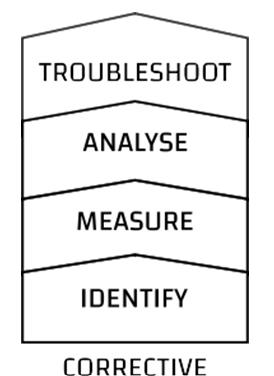
This approach involves identifying defects, such as porosities, and analyzing their root causes when they fall outside customer specifications. It’s a reactive approach taken in response to in-process rejections or customer-reported issues.
Preventive Approach
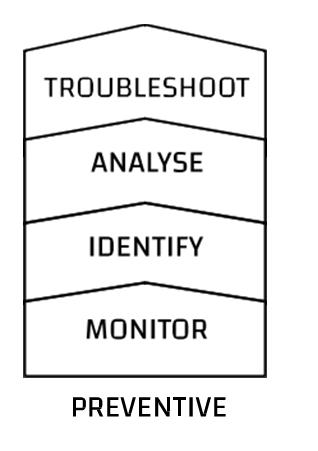
The preventive approach aims to minimize or avoid rejections altogether. It involves monitoring key design and process parameters regularly. If deviations beyond acceptable limits are observed, a thorough analysis is conducted to identify and rectify root causes.
By adhering to the preventive approach, die casters can maintain parameters within specified limits and minimize porosity from the outset. For example, maintaining proper intensification pressure can help prevent shrinkage porosity.
Conclusion
“Unlocking Die-Casting Excellence: Zero Porosity Management” by Rahat A Bhatia opens new horizons in the world of porosity control for die casting. While acknowledging the complexities involved, it emphasizes the significance of feedback mechanisms, technological advancements, and systematic approaches to optimize the die-casting process. By embracing Industry 4.0, AI, and the principles of the Design and Optimization Cycles, die casters can journey towards excellence, achieving the elusive goal of zero porosity.
